M Series Connectors
Are lightweight triplestart ratchet coupling type connectors designed for avionics, aerospace, Harsh Environment Connectors, security, motorsport and heavy duty applications.
The M12 connector is not a new product; everyone is used to classifying it as a European standard connector. Now it has developed into a complete system. From the number of Pins up to 17 Pins, and has a lot of interface types, also known as the code. Currently, our domestic mainstream on the most used A code which 4, 5 Pin two specifications of the largest use; sensors, IO, etc., for the primary application industry.
M12, because there is no critical anti-misplaced design, can only achieve anti-misplaced by increasing the code of interface. But now, the interface code, in addition to anti-misplaced, some have also become industry-specific interfaces. For example, D code, X code, and S code.

Although the M12 Connector has been on the market for many years, its 6 Pin has always been a mystery. Whether it is Phoenix or Pentax, and later Harting in their product manuals have not found this 6 Pin trace. Domestic counterparts have done 6 Pin, but often can not be inter-matched with the equipment side. Cases sent to the United States, and the local 6 Pin can not be interoperable, were all returned. 6 Pin in the end, what happened?
We have to look at the standard to find the answer to this question.
M12 products are implemented IEC6107-2-101, the latest version of which can be found in April 2012. Which is a detailed definition of the M12 A, B, C, D, and P interface codes of products. Where A code according to the structure, plug, and socket, male and female factors into 36 product categories; code B is 8 categories; code C is 27 categories; code D is a 4 Pin; code P is a 5 Pin.
Among them, code A is a 6-Pin, but I feel that it is a new addition. The picture of 6 Pins in the standard looks like this.

The original 8 Pin is the last article on the current page, 6 Pin placed in the first article on the second page, and the picture quality is also very poor. I think it should be the reason for the later addition. The original article added a NOTE to the 6 Pin.
The original text is as follows.
NOTE2: The 6 and 7 way connectors are partially loaded variants of the 8 way connector.
It means that 6 and 7 Pins refer to the Pin spectrum of 8 Pin connectors
Let’s look at the 8-Pin Pin spectrum.
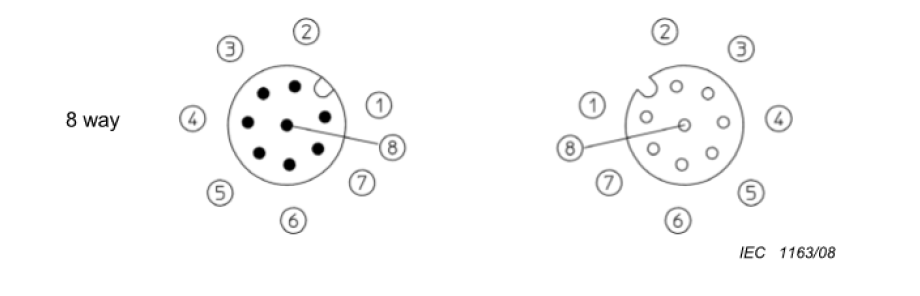
Combined with the two pictures, it can be deduced that the 6 Pin is the 8 Pin to remove the 5 and 8 Pin numbers. 7 Pin is to remove the 8 Pin number. In addition to the 6 Pin, the standard also added to the 9 Pin, and 11 Pin specifications, but these two specifications shipped less; here will not go into detail.
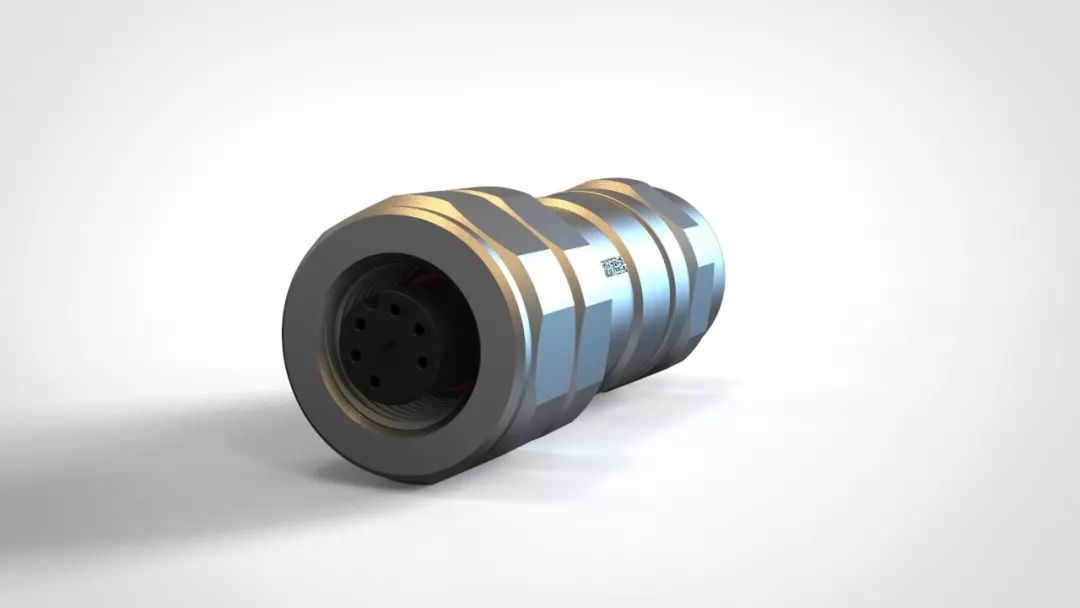

A-code of the 6 Pin effect
In 2012, IEC made the standard specification. But this 6 Pin is the standard 6 Pin of M12? Sorry, there are two standards of M12 Connector 6 Pin; the other is the C code 6 Pin.
C code is a more interesting code. From 5 Pins, the contact body diameter is changed according to the American standard to 0.76mm diameter. And C-code Pin spectrum only to 6 Pins, this point must be noted.
There are two codes of C-code contact body, 1.0mm and 0.76mm, while A-code is 0.8mm from 6 Pins and 0.6mm from 9 Pins.
Another special feature of the C code is that it has a PE position, which is the grounding position. This grounding pin is 1mm longer than the conventional pin. I know less about this, the application industry I have not understood clearly.
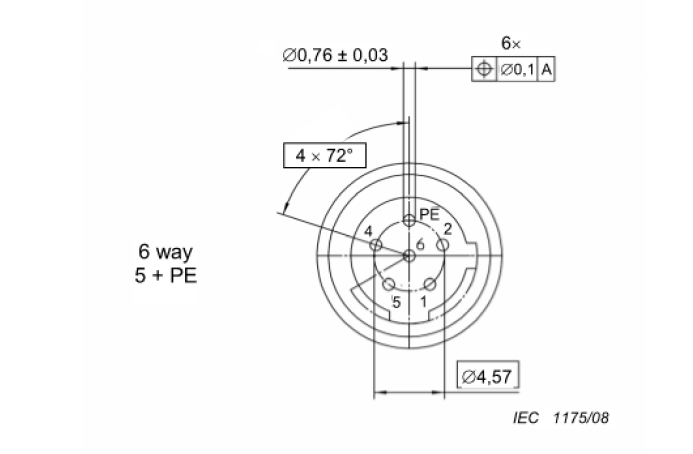
Pin spectrum diagram of C-code 6 Pins
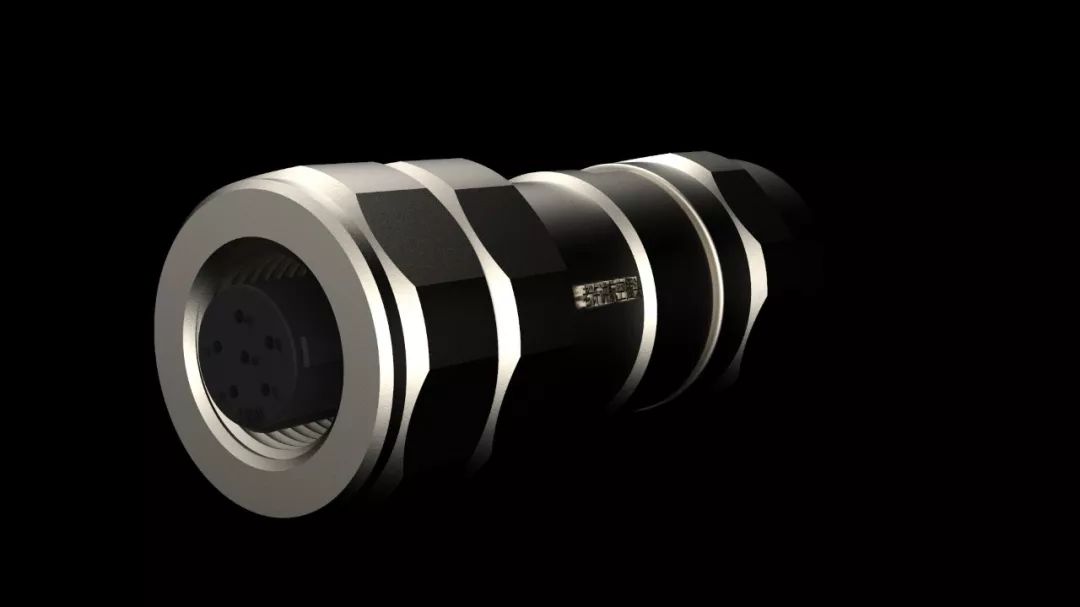

Effect diagram of C code
M12 6 Pin to bring confusion, or we did not find the main standard caused by. Connector will increasingly develop in the direction of standardization, I hope that peer friends, find more standards, and timely update the standards document. This can adapt to the needs of foreign trade development.
Finally, post two more, the M12 effect.

